Data democratization is revitalizing industrial manufacturing operations, enabling better decision-making, and improving operational efficiency. Learn how making data accessible to all employees can drive significant cost reductions and uncover new revenue streams.
Industrial manufacturers are constantly looking for ways to enhance profitability and maintain operational efficiency. It’s a delicate balance. One of the most effective strategies is leveraging data to inform decision-making processes, but many organizations struggle with harnessing the full potential of their data. They’re battling challenges like fragmented data management systems and poor data quality. The more time they spend fighting their data, the more they hinder cost reduction efforts and limit opportunities for revenue growth.
Data democratization offers a promising solution. By empowering employees with the right data at the right time, organizations can foster a culture of informed decision-making and innovation. But how can companies ensure data quality and manage the vast volumes of information generated daily? Let’s look at some key obstacles data democratization helps solve when it comes to reducing costs and increasing revenues, improving data management, and tackling data quality issues.
Reducing Costs and Increasing Revenues through Democratized Data
Data democratization means making data accessible to everyone within an organization, regardless of their technical expertise. This approach aims to break down data silos, ensuring that valuable information is available to all employees who need it to make informed decisions. By providing widespread access to data, organizations can empower their workforce to act on insights and drive better business outcomes.
- Empowering Decision-Making with Data Accessibility: Enhances decision-making processes across the organization by reducing bottlenecks caused by data silos and enabling quick, effective decisions at all levels. Examples include marketing teams adjusting campaigns using real-time sales data and operations teams optimizing supply chain processes.
- Cost Reduction through Data-Driven Strategies: Identifies inefficiencies and optimizes operations through predictive maintenance, reducing downtime and maintenance costs, and data analytics pinpointing underperforming areas. For example, a retail company can use data analytics to optimize inventory management, reducing excess stock and minimizing storage costs.
- Increasing Revenues with Data Insights: Opens up new avenues for revenue generation by providing insights into customer behavior, market trends, and operational performance. E-commerce platforms, for instance, can personalize shopping experiences by analyzing browsing history and purchase behavior, tailoring offerings to meet demand more effectively.
- Uncovering New Business Opportunities: Facilitates identifying new business opportunities by encouraging collaboration between departments. For example, sales and product development teams can identify emerging market trends and develop new products or services.
Hypothetical Case Study: Success through Data Democratization
Suppose a leading global logistics company implemented a data democratization strategy to improve operational efficiency and customer service. Before implementing this strategy, it struggled with siloed data, leading to inefficiencies such as delayed deliveries, suboptimal route planning, and poor customer satisfaction. The lack of accessible data led to higher operational costs and decreased customer retention.
The company democratized its data to address these issues, providing employees with real-time access to shipment statuses, delivery routes, and customer feedback. This strategy enabled the company to:
- Reduce delivery times by tracking shipments in real time and making prompt adjustments.
- Optimize routes using traffic pattern analysis for more efficient delivery schedules.
- Enhance customer satisfaction through quick issue resolution and accurate shipment updates.
This approach significantly reduced operational costs and increased customer retention and revenue. By breaking down data silos and empowering employees with critical information, the company transformed its operations and achieved substantial business benefits.
Effective Data Management: The Backbone of Data Democratization
Robust data management systems are essential for successful data democratization. They ensure data is organized, accessible, and reliable, supporting informed decision-making across the organization. Integrating data from various sources provides a comprehensive view, enhancing insights and decision-making capabilities.
Best practices for data management in a democratized environment include:
- Establishing strong data governance: Implementing policies and procedures to maintain data quality, security, and compliance.
- Conducting regular data audits: Identifying and rectifying inaccuracies and inconsistencies.
- Utilizing metadata: Providing context and improving data discoverability and usability.
Technology plays a vital role in data management:
- IoT and cloud computing: Enable real-time data collection and storage, facilitating access and analysis from anywhere.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): Automates data processing, enhances accuracy, and generates actionable insights.
- Data management platforms: Centralize data storage and processing, offering tools for integration, quality control, and analytics.
Streamlined data management improves operational efficiency by reducing the time spent searching for data, allowing employees to focus on analysis and decision-making. It enhances collaboration by promoting data sharing across departments and increases security through centralized control and monitoring.
Related: The Foundation of Modern Manufacturing: IoT and Enterprise Connectivity
Ensuring Data Quality in a Democratized Data Environment
Poor data quality doesn’t just prevent companies from improving cost and revenue—it actively costs them money in the long run. Gartner published in 2021 that poor data quality was costing companies an average of about $12.9 million per year. Each.
Common Data Quality Issues:
- Inaccurate Data: Errors in data entry, outdated information, and inconsistent data formats.
- Incomplete Data: Missing values or gaps in datasets that can skew analysis.
- Duplicate Data: Redundant data entries that lead to confusion and inefficiency.
Strategies to Ensure High Data Quality:
- Data Governance Framework: Implement policies and procedures to maintain data quality standards, including validation and cleansing processes.
- Regular Audits and Monitoring: Conduct periodic reviews to identify and correct data quality issues, ensuring data remains accurate and up-to-date.
- Employee Training and Awareness: Educate employees on the importance of data quality and best data entry and management practices.
- Use of Data Quality Tools: Leverage software solutions for data profiling, cleansing, and enrichment to automate and streamline quality control.
Addressing Data Quality Issues: Challenges and Solutions
Ensuring high data quality is an ongoing process that requires a proactive approach to identifying, addressing, and resolving issues.
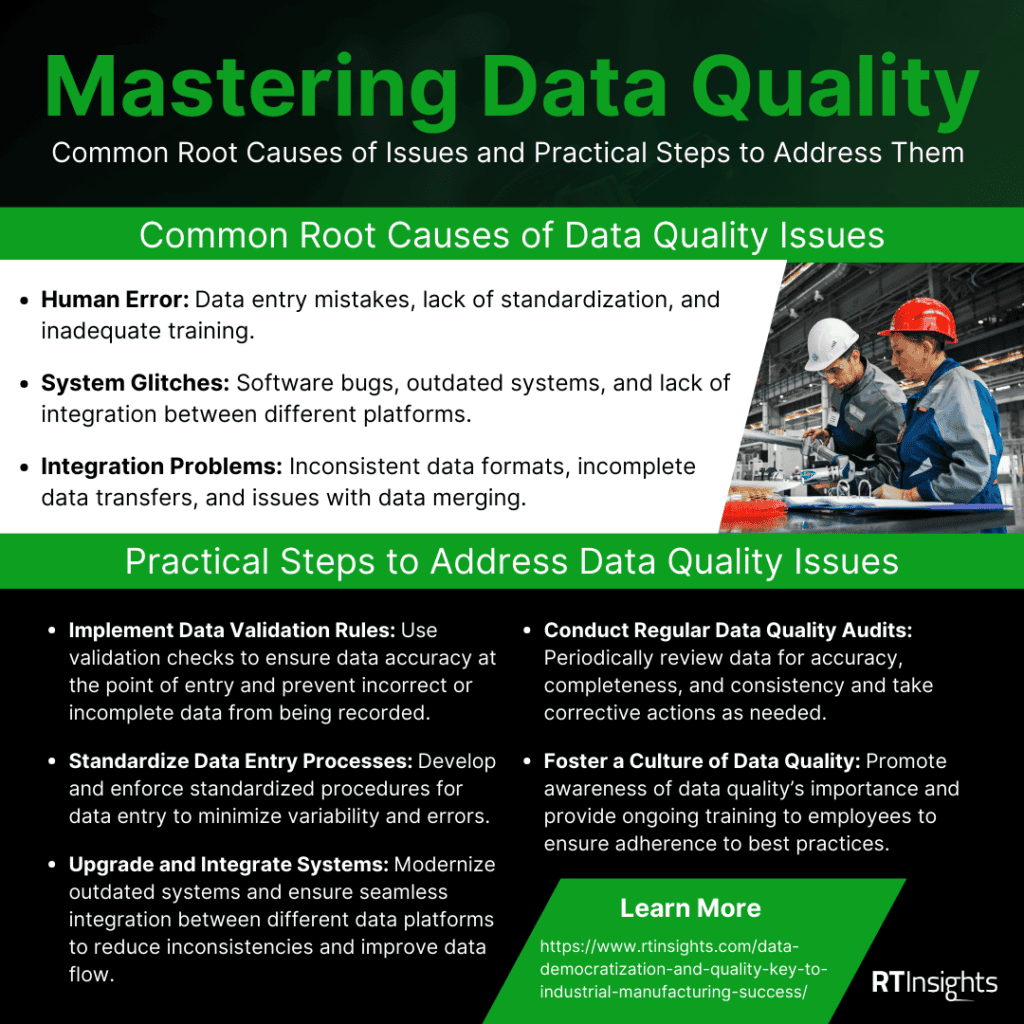
Identifying Root Causes of Data Quality Issues:
- Human Error: Data entry mistakes, lack of standardization, and inadequate training.
- System Glitches: Software bugs, outdated systems, and lack of integration between different platforms.
- Integration Problems: Inconsistent data formats, incomplete data transfers, and issues with data merging.
Practical Steps to Address Data Quality Issues:
- Implement Data Validation Rules: Use validation checks to ensure data accuracy at the point of entry and prevent incorrect or incomplete data from being recorded.
- Standardize Data Entry Processes: Develop and enforce standardized procedures for data entry to minimize variability and errors.
- Upgrade and Integrate Systems: Modernize outdated systems and ensure seamless integration between different data platforms to reduce inconsistencies and improve data flow.
- Conduct Regular Data Quality Audits: Periodically review data for accuracy, completeness, and consistency and take corrective actions as needed.
- Foster a Culture of Data Quality: Promote awareness of data quality’s importance and provide ongoing training to employees to ensure adherence to best practices.
Don’t Forget Employee Training and Awareness:
- Training Programs: Develop comprehensive training programs to educate employees on data quality and proper data management practices.
- Ongoing Support and Resources: Provide continuous support and resources, including documentation, workshops, and access to data quality tools.
- Accountability and Ownership: Encourage employees to take ownership of data quality by establishing clear roles and responsibilities.
Maximizing the Potential of Democratized Data
Ensuring high data quality and effective management are crucial to leveraging democratized data. By implementing robust data governance frameworks, utilizing advanced tools and technologies, and fostering a culture of data quality awareness, industrial manufacturers can harness the full potential of their data. This approach enhances decision-making and operational efficiency and drives innovation and competitive advantage, ultimately leading to reduced costs and increased revenues.